explain
pain
section
3
page
62
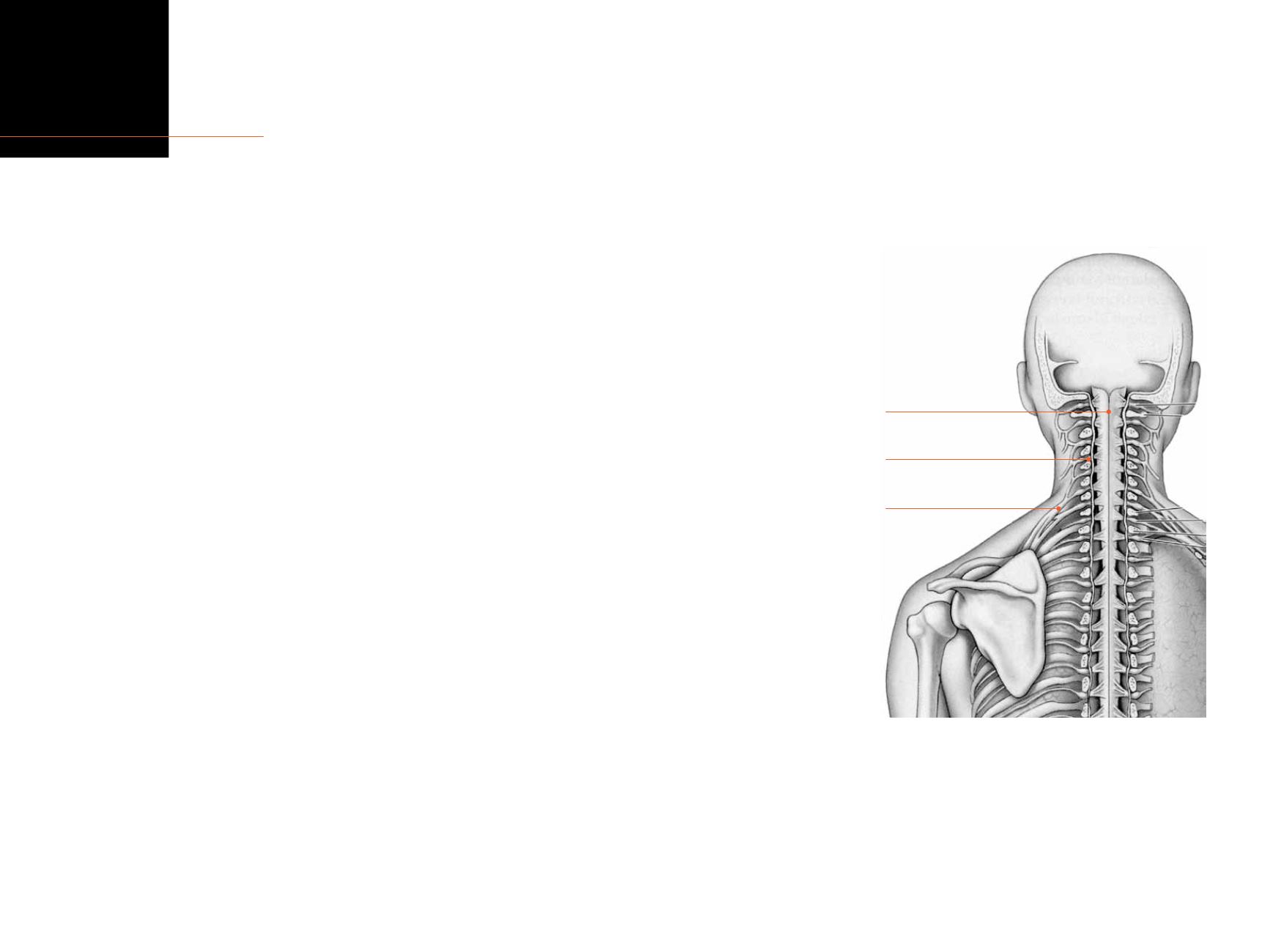
T
here is a little bulge in the peripheral nerve just where it is about to
enter the spinal cord. This bulge is important because it contains the
nuclei of the neurones. The bulge is called the dorsal root ganglion (DRG).
It is effectively a ‘minibrain’ because it is the first place that messages
coming in from your tissues can undergo somemodulation and evaluation.
You could say it is themost peripheral place inwhich you think!
Some interesting features of the DRG
1.
All the sensory neurones that make up the peripheral nerve have their
nucleus (control centre) in the DRG. The nucleus is where the DNA of
the neurone resides, ready to be activated to start making sensors,
which are transported to the rest of the neurone (see page 30). This
means that anything that affects the DRG can have profound effects on
thewhole peripheral nerve, including changes in transmission and
manufacture of sensors.
103
2.
The DRG is really sensitive and changeable. Whennerves are injured,
neurones sprout in the DRG and can lead to all sorts of ‘short
circuits’.
104,105
The boneswhichusually protect the DRG can sometimes
actually interferewith it.
106,107
Fluids such as blood and ‘inflammatory
soup’ (say, produced by a soft tissue injury nearby) can irritate it.
108
Sometimes, when there are arthritic changes in the joints nearby, and
you bend your head back, the DRG can be squeezed by the bones around
it. Because the DRG is so sensitive, this sort of thing can really hurt. No
wonder some peoplewithneck painhold their head forward.
Adapted from Bear et al.
111
spinal cord
peripheral nerve
drg
The dorsal root ganglion – the peripheral
nerve’sminibrain


